Every week around 500 children under five are rushed to hospital because it's thought they have swallowed something poisonous. Most poisoning accidents involve medicines, household products and cosmetics. The most common form of poisoning is from medication.
-
Keep medicines high up and out of reach.
-
Keep anything that may be poisonous out of reach - this includes all medicines and pills, alcohol, household cleaners, liquid washing tablets and garden products, preferably in a locked cupboard.
-
Use containers that have child-resistant tops - be aware that by the age of three, many children are able to open child-resistant tops.
-
Keep all dangerous chemicals in their original containers - for example, do not store weedkiller in an old drinks bottle as a young child may mistake it for something safe to drink.
-
Discourage your children from eating any plants or fungi when outside. Avoid buying plants with poisonous leaves or berries.
-
Keep alcohol out of the reach of children. Even a small amount can cause alcohol poisoning in children.
Babies and toddlers can easily swallow, inhale or choke on small items like marbles, beads, lolly sticks, balloons, peanuts, buttons, nappy sacks, plastic toy pieces, strings or cords.
PREVENTION:
Babies can suffocate or choke on nappy sacks, keep all plastic bags out of reach.
-
Check that toys with small pieces are not left out for a toddler to chew and choke on.
-
Check that toys are age appropriate, in good condition and include toy safety marks.
-
Find out more about resuscitation (CPR) visit
www.redcrossfirstaidtraining.co.uk
WHAT TO DO:
Act immediately and calmly.
If you can see the object, try to remove it. But don’t poke blindly with your fingers. You could make things worse by
pushing the object in further.
If your child is coughing loudly, there is no need to do anything. Encourage them to carry on coughing and don’t leave them.
If your child’s coughing is not effective (it’s silent or they cannot breathe in properly), shout for help immediately and check whether they are still conscious.
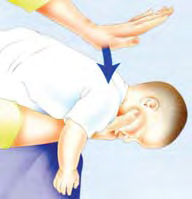
If your child is still conscious but either they are not coughing or
their coughing is not effective, use back blows.
If they become unconscious, call for help (do not leave your child
alone) and start CPR.
1
You think your child has swallowed a harmful medicine or chemical including batteries or a magnet.
2
Find the bottle or packet and take it with you when you seek medical help.
3
Immediately contact your pharmacist, GP, go to A&E or call NHS 111.